PFAS Waste Management in Landfills to Minimize Environmental Harm
PFAS Waste Management in Landfills to Minimize Environmental Harm
Blog Article
Advanced Techniques for Efficient PFAS Contamination Removal
The relentless challenge of PFAS contamination requires the exploration of sophisticated removal approaches that can effectively deal with these unsafe substances. Innovative technologies, such as sophisticated oxidation processes and different adsorption methods, have arised as promising solutions in mitigating PFAS from impacted settings. The duty of governing frameworks in forming these innovations can not be ignored, as they dictate the pace and direction of removal efforts. As we assess these innovative methods, it ends up being essential to evaluate their useful applications and the broader implications for environmental health and wellness and plan.
Recognizing PFAS Features
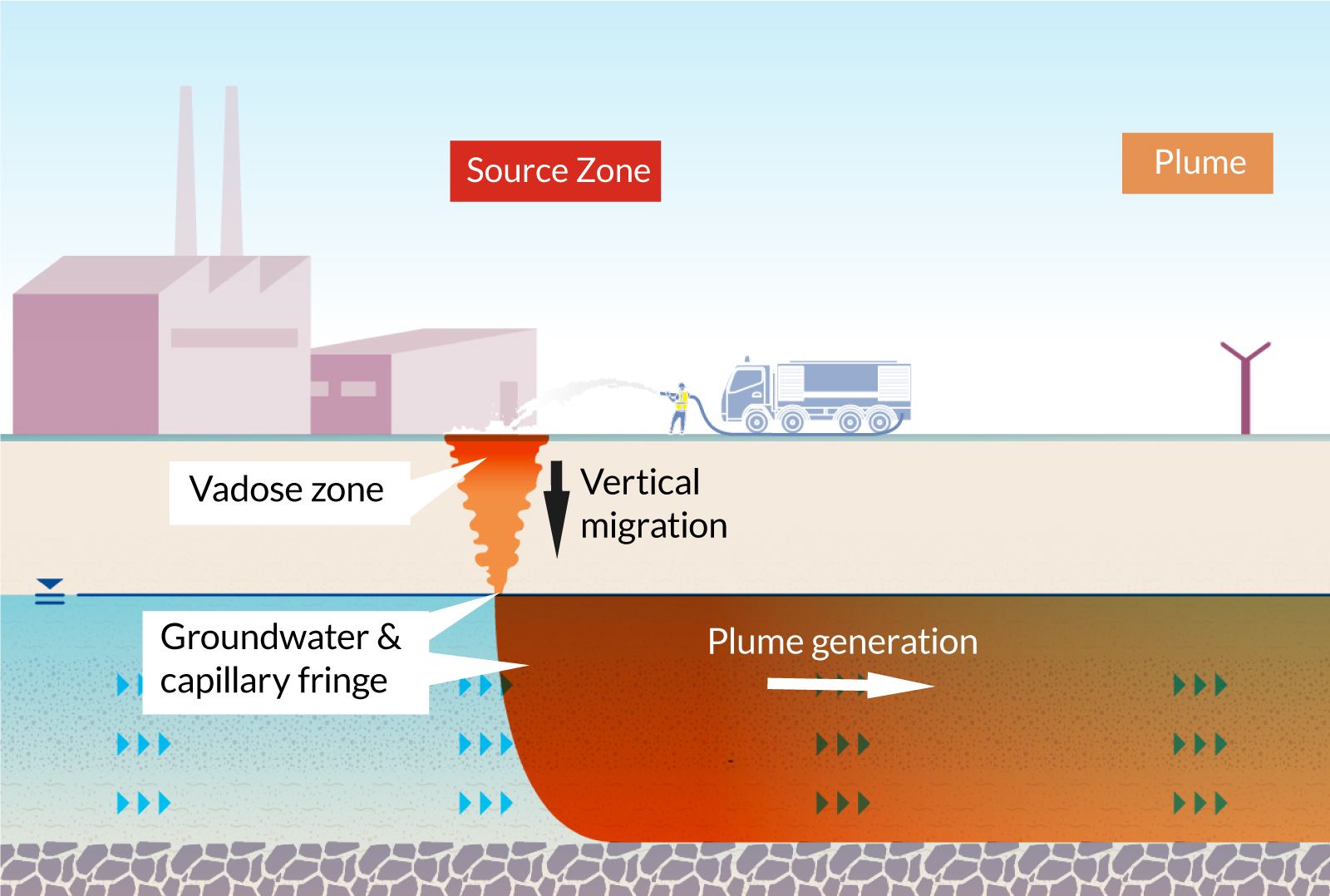
Although per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have actually been widely made use of in various industrial and consumer products as a result of their special homes, their perseverance in the setting poses substantial obstacles to public health and safety. PFAS are a team of synthetic chemicals defined by a carbon-fluorine bond, among the greatest chemical bonds recognized, which adds to their phenomenal security and resistance to degradation. This stability permits PFAS to collect in the environment and living organisms, bring about potential damaging health results.
The hydrophobic and oleophobic nature of PFAS makes them especially effective in applications such as non-stick layers, stain-resistant fabrics, and firefighting foams. These same residential properties contribute to their ecological perseverance, as PFAS do not easily damage down through all-natural processes. Moreover, their prevalent use has resulted in common contamination of water resources and soils, complicating remediation initiatives. Comprehending the chemical homes of PFAS is important for developing efficient methods to handle and alleviate their ecological effect. The one-of-a-kind qualities of these materials require a nuanced approach to attend to the difficulties postured by their visibility in environments and prospective human exposure.
Ingenious Removal Technologies
The determination of PFAS in the setting has spurred the advancement of cutting-edge removal technologies aimed at effectively removing these pollutants from affected environments. Among one of the most appealing methods are sophisticated oxidation procedures (AOPs), which make use of effective oxidants to damage down PFAS compounds into less damaging substances. AOPs can be tailored to target particular PFAS structures, boosting their efficacy.
One more emerging technology is the usage of adsorption media, such as activated carbon and ion exchange materials, which can selectively record PFAS from contaminated water. These materials have revealed significant removal effectiveness, although routine replacement and regrowth are needed to keep performance.
Membrane filtration strategies, including reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, are additionally gaining traction in PFAS remediation. These techniques can properly divide PFAS from water, giving a sensible option for treating polluted sources. In addition, thermal treatment methods, such as incineration, can decay PFAS right into safe byproducts, though they need cautious monitoring to regulate emissions.
Collectively, these ingenious remediation technologies represent significant advancements in the recurring battle versus PFAS contamination, using numerous approaches to restore afflicted atmospheres and safeguard public health.

Bioremediation Techniques
Bioremediation methods use an appealing approach to addressing PFAS contamination by taking advantage of the all-natural abilities of microbes to degrade these relentless compounds (m270 waste management). This method entails making use of germs, fungis, and various other microorganisms that can metabolize or change PFAS substances into less hazardous byproducts
Current advancements in molecular biology and ecological microbiology have actually boosted our understanding of microbial areas and their possible roles in PFAS deterioration. Researchers are actively discovering specific strains of germs, such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus, which have actually shown the ability to break down particular PFAS compounds.
Sitting bioremediation techniques, where microorganisms are stimulated directly in polluted settings, can be specifically reliable. This technique usually involves the application of nutrients or electron benefactors to advertise microbial growth and activity. Additionally, ex-spouse situ techniques, such as bioreactors, permit for regulated problems that can optimize degradation prices.
In spite of the pledge of bioremediation, challenges continue to be, including the complicated nature of PFAS substances and the need for considerable area screening - m270 waste management. Continued research and advancement will certainly be vital to improve these methods and evaluate their effectiveness in varied ecological contexts
Adsorption and Filtering Methods
Attending to PFAS contamination typically includes using adsorption and filtration methods, which are developed to remove these relentless chemicals from use this link water and dirt. Among the various strategies, turned on carbon adsorption is extensively used because of its high area and porosity, allowing efficient capturing of PFAS More Bonuses molecules. Granular turned on carbon (GAC) systems are specifically favored for treating big volumes of polluted water, while powdered triggered carbon (PAC) can be used for smaller-scale applications.
Ion exchange materials also show assurance in PFAS removal, operating by exchanging PFAS ions with much less damaging ions in the water. This method has demonstrated performance in concentrating PFAS compounds, promoting their succeeding elimination. In addition, membrane layer filtration strategies, such as reverse osmosis and nanofiltration, operate by utilizing semi-permeable membranes to separate PFAS from water, properly reducing their focus.
While these approaches work, they need to be meticulously chosen based upon the specific PFAS substances existing and the environmental context. Constant innovations in materials scientific research and engineering are leading to the advancement of unique adsorbents and purification systems that improve elimination effectiveness and lower functional costs, therefore enhancing overall removal efforts.
Regulatory and Policy Considerations
How can reliable regulative frameworks enhance the administration of PFAS contamination? Extensive policies are crucial to make certain a coordinated and robust action to the challenges postured by per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) Regulations can establish clear standards for monitoring, reporting, and remediating PFAS-contaminated websites, fostering liability amongst sectors and public entities. (m270 waste management)
In addition, monetary incentives and gives can be integrated into policies to encourage the fostering of sophisticated remediation modern technologies. Policymakers ought to also focus on r & d, ensuring that arising approaches for PFAS removal are confirmed and carried out efficiently.
Additionally, public recognition and engagement are critical parts of any type of regulative technique, equipping neighborhoods to support for their health and wellness and safety. Eventually, a well-structured regulative atmosphere will not just enhance the management of PFAS contamination yet likewise advertise sustainable techniques that protect future generations.
Conclusion
In summary, the intricacy of PFAS contamination necessitates the adoption of sophisticated removal techniques. Continued study and development in this area remain crucial to dealing with the difficulties posed by PFAS contamination.
Report this page